Data
We will use an example (random) tree that comes with the package.
tree <- ape::read.tree(system.file(
"extdata/crb_tree_15_tips.tre", package = "treepplr"))
ape::plot.phylo(tree, cex = 0.5)
axisPhylo()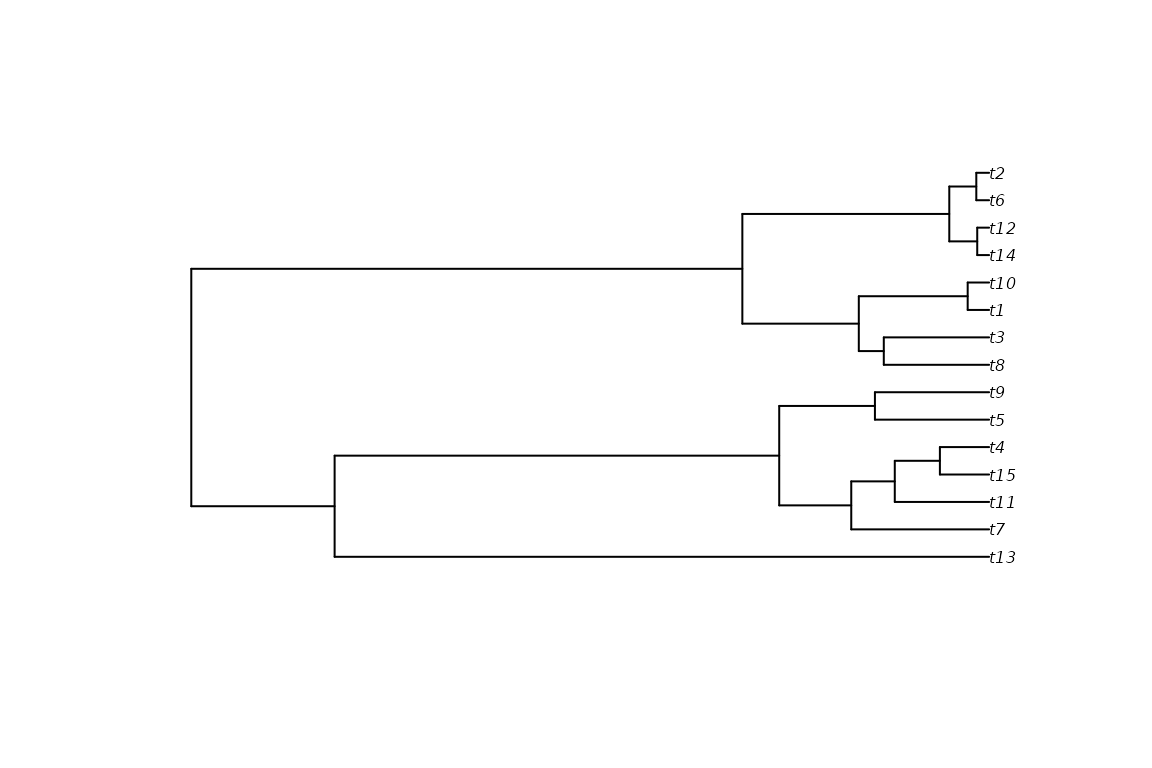
We need to convert the tree to a TreePPL readable format and read the CRB model.
data <- tp_phylo_to_tpjson(tree, age="tip-to-root")
model <- tp_model(system.file("extdata/crb.tppl", package = "treepplr"))Run treeppl
Compile and run the TreePPL program with standard inference settings.
output_list <- tp_treeppl(model = model, data = data)Plot posterior
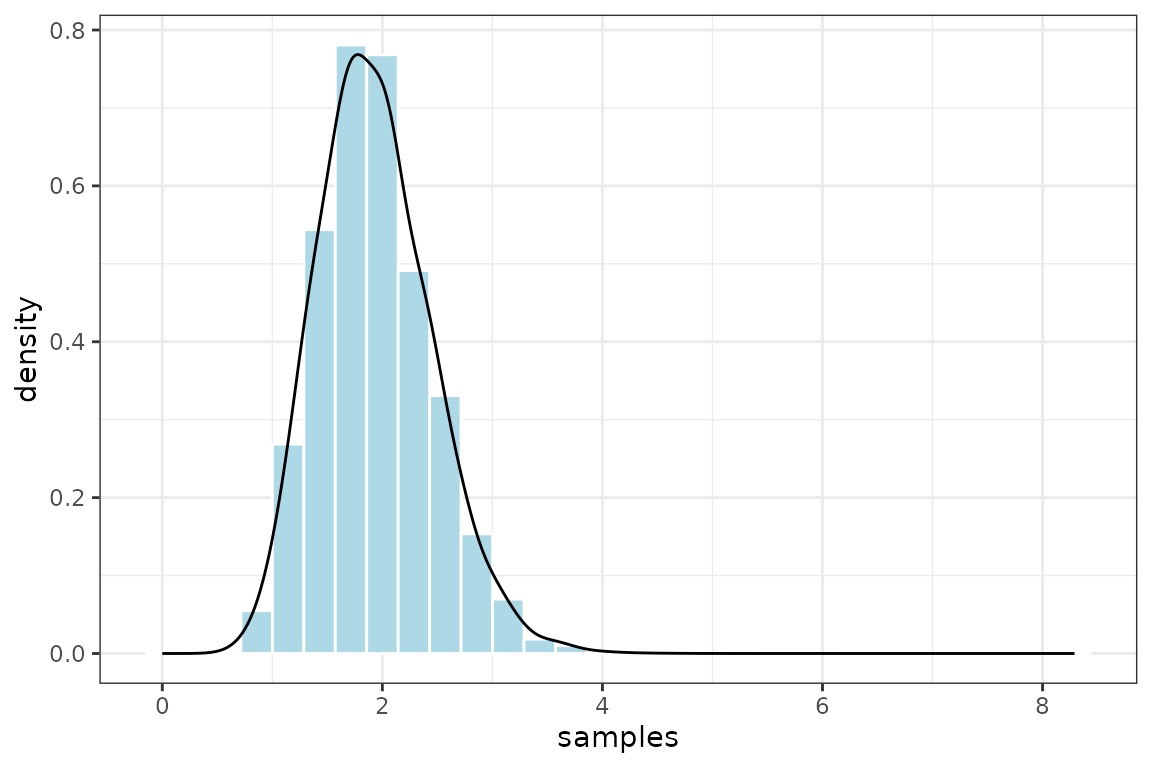
TreePPL outputs the log weight of each sample, so first we need to get the normalized weights and then we can plot the posterior distribution produced.
# turn list into a data frame where each row represents one sample
# and calculate normalized weights from log weights and normalizing constants.
output <- tp_parse(output_list) %>%
dplyr::mutate(total_lweight = log_weight + norm_const) %>%
dplyr::mutate(norm_weight = exp(total_lweight - max(.$total_lweight)))
ggplot2::ggplot(output, ggplot2::aes(samples, weight = norm_weight)) +
ggplot2::geom_histogram(ggplot2::aes(y = ggplot2::after_stat(density)),
col = "white", fill = "lightblue", binwidth=0.04) +
ggplot2::geom_density() +
ggplot2::theme_bw()